
NanoBat
GHz nanoscale electrical and dielectric measurements
of the solid-electrolyte interphase
and applications in the battery manufacturing line
of the solid-electrolyte interphase
and applications in the battery manufacturing line
STAND-ALONE TEACHING KIT
FOR NANOMETER 1D SPACE FILLED WITH AN ELECTROLYTE AND BOUNDED BY TWO ELECTRODES
FOR NANOMETER 1D SPACE FILLED WITH AN ELECTROLYTE AND BOUNDED BY TWO ELECTRODES
Download Stand-Alone ElectroLyte Teaching Kit.
Download Stand-Alone ElectroLyte Teaching Kit dedicated manual.
Download Stand-Alone ElectroLyte Teaching Kit dedicated manual.
The PDD1 software simulates a nanometer 1D space filled with an electrolyte and bounded by two electrodes. In such a system there is a physical phenomenon of the flow of ions. In simulation separate currents are taken into account for positive and negative ions. They combine the influence of the existing electric field on the charges with the diffusion process due to charge distribution. Electric potential at the two electrodes is defined by the user and it is constant during the simulation, thus satisfying the Dirichlet boundary condition. After the user enters the rest of the initial conditions, the calculations of the currents , charges and electric potential begin using the FDTD algorithm. Added a new option to start an algorithm from a user-defined distribution of positive and negative charges. By starting the algorithm with a regular distribution of electric charges, it becomes irregular as a result of the applied potential difference. This distribution can be saved and loaded as a starting condition. After solving such a system without drift–diffusion equations, the same electric potential distribution is obtained. The newly created software generates results comparable to already existing solutions. Additionally, a new possibility has been introduced to start calculations with an irregular distribution of electric charges. The application is available in open access, this will facilitate teaching in academia and dissemination in industry, in line with European open research policy.
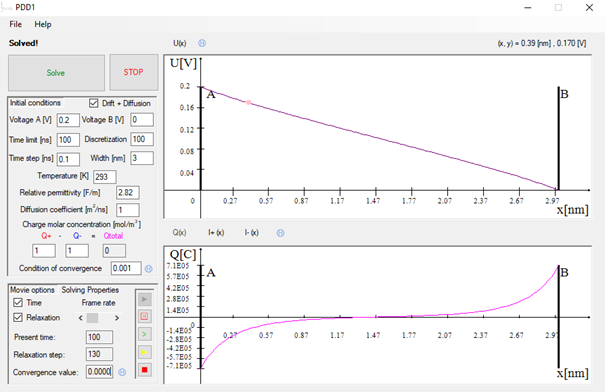
PDD1 application.
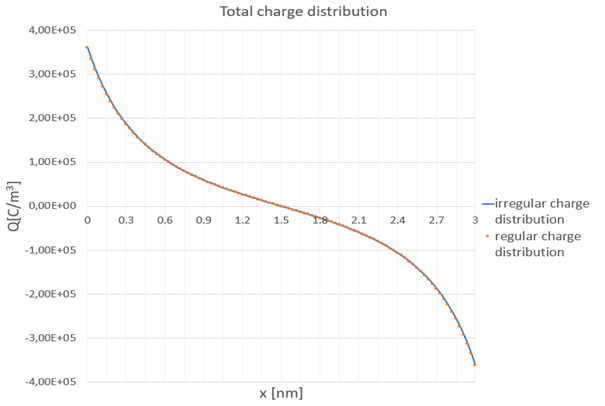
Comparison of total charge with a different initial charge distribution.

The NanoBat project has received funding from the European Union's Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under grant agreement No 861962.
