
NanoBat
GHz nanoscale electrical and dielectric measurements
of the solid-electrolyte interphase
and applications in the battery manufacturing line
of the solid-electrolyte interphase
and applications in the battery manufacturing line
INITIAL MATERIAL CHARACTERISATION
In the first Project stage, QWED and PLEIONE have chosen dielectric materials, which could potentially serve as a substrate material for graphene-based composite layers for their initial EM characterisation with QWED’s test-fixtures. The substrate materials have been evaluated in terms of their electric losses, which need to be at a very low level to ensure high accuracy of further graphene layers characterisation.
The measurement campaign involved four samples delivered by PLEIONE:
The measurement campaign involved four samples delivered by PLEIONE:
•
Two, commercially available dielectric materials serving as reference samples: quartz (left) and polymer (right).

•
Two graphene-based composite samples deposited on reference materials (on quartz – left; on polymer – right), manufactured by PLEIONE.

Substrate Measurements
Note: Thickness measurements were performed with the aid of a hand held micrometer.
Electromagnetic parameters of the reference materials, measured with the aid of QWED Split-Post Dielectric Resonators (SPDRs) are gathered in Table 1. Materials were measured at three frequencies (with three different SPDR units) and as a result electric permittivity and losses were delivered.
Note: Thickness measurements were performed with the aid of a hand held micrometer.
Electromagnetic parameters of the reference materials, measured with the aid of QWED Split-Post Dielectric Resonators (SPDRs) are gathered in Table 1. Materials were measured at three frequencies (with three different SPDR units) and as a result electric permittivity and losses were delivered.
Table 1. Electric permittivity and losses of quartz and polymer material samples measured with SPDRs at different frequencies.
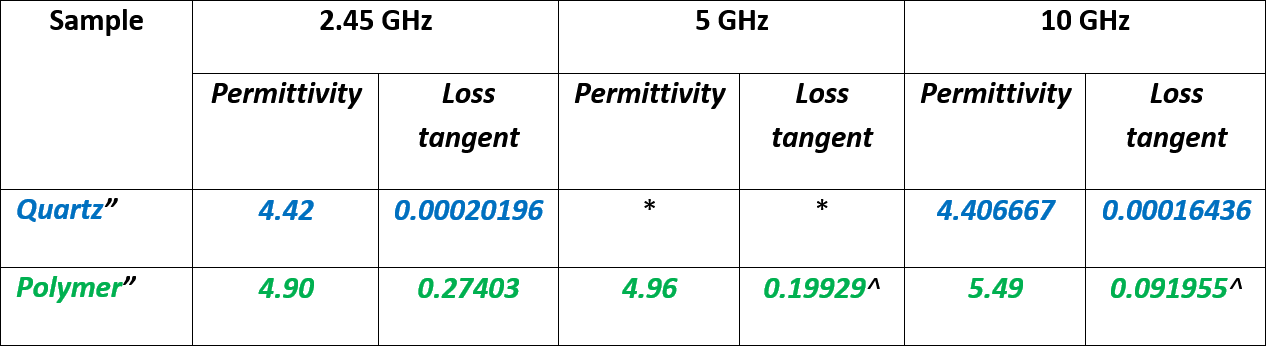
'' measurements performed for averaged sample thickness
* sample is too large to fit 5GHz SPDR
^ attenuation of the measurement signal is significant -> extraction of the losses is subject to high error
* sample is too large to fit 5GHz SPDR
^ attenuation of the measurement signal is significant -> extraction of the losses is subject to high error
As expected, the dielectric losses of quartz material are very low (loss tangent ca. 10-4) making it a very good substrate material for initial characterisation of thin conductive layers (deposited on a host substrate) with QWED’s measurement techniques.
From the measurement of polymer material it is seen that the microwave signal is significantly attenuated in the presence of polymer material at each of the considered frequencies (see ZIP file with raw measurement data). The attenuation is especially high at 5GHz and 10GHz, which causes extraction uncertainties when using SPDR device.
Conclusions:
Based on electromagnetic parameters of reference materials (electric permittivity and losses) it is recommended that the substrate material for graphene based anodes deposition, for characterisation with QWED SiPDR technique, is quartz.
From the measurement of polymer material it is seen that the microwave signal is significantly attenuated in the presence of polymer material at each of the considered frequencies (see ZIP file with raw measurement data). The attenuation is especially high at 5GHz and 10GHz, which causes extraction uncertainties when using SPDR device.
Conclusions:
Based on electromagnetic parameters of reference materials (electric permittivity and losses) it is recommended that the substrate material for graphene based anodes deposition, for characterisation with QWED SiPDR technique, is quartz.
Graphene Layers Measurements
PLEIONE’s graphene-based composite (GNP) layers (graphene anodes) deposited on reference materials (quartz and polymer) were characterised with the aid of QWED SiPDR, operating at 5GHz. Layers are characterised with surface resistance [ohm/square]. The layers were measured in the middle of material sample and near the sample edge.
PLEIONE’s graphene-based composite (GNP) layers (graphene anodes) deposited on reference materials (quartz and polymer) were characterised with the aid of QWED SiPDR, operating at 5GHz. Layers are characterised with surface resistance [ohm/square]. The layers were measured in the middle of material sample and near the sample edge.
Table 2. Surface resistance of GNP layers measured with SiPDR at 5GHz.
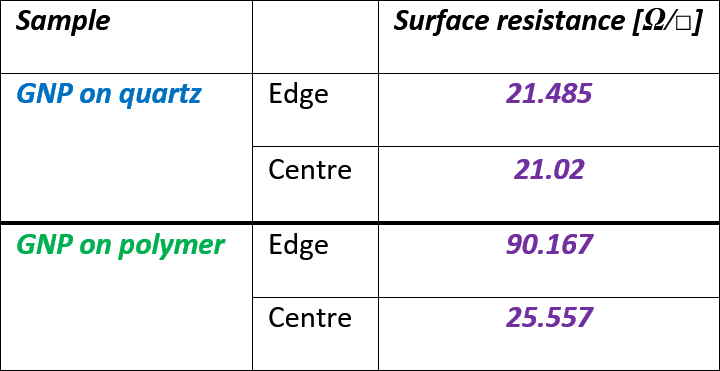
Based on the results gathered in Table 2, deposition of graphene based composite layers on stiff substrate material (quartz) allows for achieving higher homogeneity in electric parameters of the layer than in the case of non-stiff substrates as polymer.
Conclusions:
For the purpose of achieving highest possible uniformity of the surface resistance across the layer and accuracy of its measurement it is recommended that the graphene layers are deposited on stiff, low-loss substrate materials as quartz.
Conclusions:
For the purpose of achieving highest possible uniformity of the surface resistance across the layer and accuracy of its measurement it is recommended that the graphene layers are deposited on stiff, low-loss substrate materials as quartz.
The NanoBat project has received funding from the European Union's Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under grant agreement No 861962.

